Advantages of mineral wool insulation
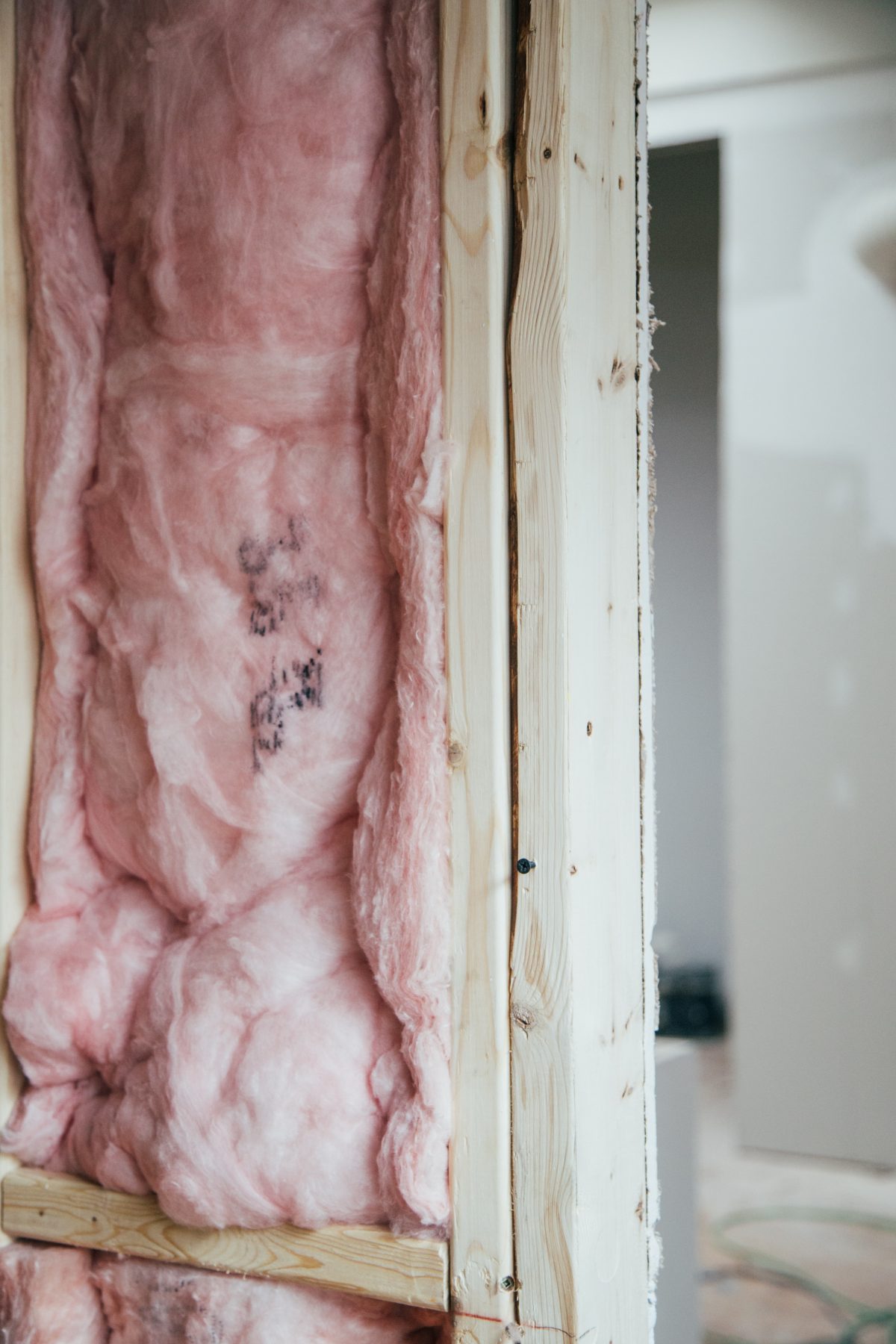
Mineral wool is often used as an insulation material because of its helpful properties, such as being affordable and easy to handle. There are two types of mineral wool, rock, and glass. They are made from slightly different materials and whilst they’re fairly similar and are often used interchangeably in certain applications, there are other situations where one will work better than the other.
In this guide, we’ll be looking at the key advantages of mineral wool insulation in relation to high-temperature measurement, so you know how it can work for your operations.
Firstly, what is mineral wool insulation?
Mineral wool includes spun yarn that is made of melted glass or stone. The threads are combined in a specific way to create a woolly structure. Then the wool is pushed down into boards or mineral wool batts that function as insulation material.
Loose wool can particularly be blown in hollow spaces like cavity walls. It is a popular product that can be used for:
- Insulating walls (with a timber frame construction)
- Insulating cavity walls and exterior walls
- Thermal and acoustic insulation of partition walls and storey floors
- Insulating attic floors
- Insulating pitched roofs and flat roofs
- Multiple industrial applications (such as machines, air conditioners, etc)
What are the advantages of mineral wool insulation?
Good thermal insulation
Mineral wool has an open fibre structure which means it can hold a large amount of air, making it a great insulator for regulating heat. The lambda value of this type of insulation is 0.03 W/mK to 0.04 W/mK, so both rock and glass wool insulation is not susceptible to thermal degradation. Therefore, it will maintain the same level of insulation over the lifetime of the building. Also, mineral wool insulation is stable, meaning it doesn’t expand or shrink. This keeps the joints between the material closed and thermal bridges to a minimum.
Fire safety
Mineral wool insulation is fully resistant to fire and doesn’t conduct heat, meaning it’s ideal for use in environments that put high demands on fire safety and industrial temperature measurement. Therefore, it is most commonly used in fire-retardant products such as partition walls, fireproof doors, ceilings, and protective clothing.
High levels of fire safety are an essential requirement for insurance companies in any type of building, and the use of fireproof insulations can in some cases be compulsory. When it comes to fire safety, mineral wool insulation is classified under Euro Class A and has the best score of all insulation materials, which is great for high temperature applications.
Impressive soundproofing
Mineral wool insulation is effective against noise pollution due to its structure and composition. There are also special acoustic tiles for ceilings, walls, and floors that absorb sound waves, making them very useful in both industrial and consumer applications.
For the latter, rock wool blankets are typically used in walls, floors, and ceilings. In the case of false or partition walls, a combination of plasterboard and mineral wool is often a good idea for absorbing sound waves. The frames need to be acoustically separated as much as possible to prevent contact bridges between the boards.
Other benefits of mineral wool insulation include it’s less expensive than other materials, it doesn’t absorb moisture, so it is immune to mould, it is fully recyclable, and it has a minimal ecological footprint. It also has a wide range of applications.
What’s the difference between glass wool and rock wool?
As previously mentioned, both glass and rock wool are very similar insulation materials. The main difference between them relates to the fibre structure. The fibres in rock (or stone) wool are shorter than glass wool, so as a result rock wool has a higher density.
Rock wool can withstand a higher pressure than glass wool. You can see the key differences between the two types of wool in the table below.
| Rock wool | Glass wool |
| Shorter fibres | Long fibres |
| High density | Lower density |
| Lambda value 0.032-0.044 W/mK | Lambda value 0.035-0.039 W/mK |
| Slightly lower fire resistance | High fire resistance |
| High elasticity | Low elasticity |
| High tensile strength | Low tensile strength |
| Melting temp 700C | Melting temp 1000C |
Conclusion
Mineral wool insulation has many advantages that make it an important part of thermal resources management. Contact our team today to discuss your heat trace and temperature measurement needs.