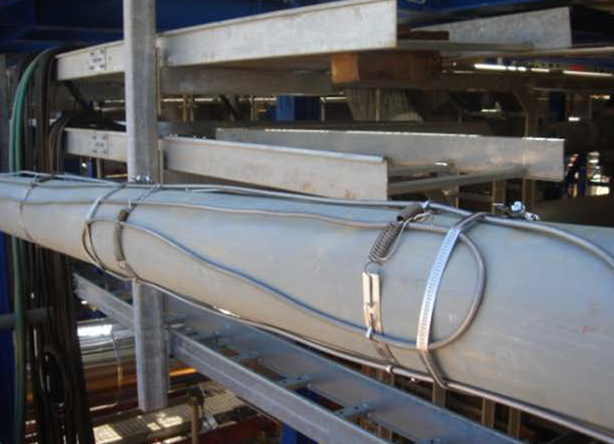
Self-regulating heat trace cables are often used to apply heat safely and efficiently for comfort, process, and maintenance purposes. They provide protection against burst water pipes, frozen roofs and gutters, ice and snow formation on ramps, paths, stairs, and many other applications.
For residential and commercial buildings, these systems offer a reliable and long-term solution to expensive damage or operational disturbances. They play such an important but often invisible role in various industries; in this article we will be exploring how self-regulating heat trace works as well as its importance.
First, what is self-regulating heat trace?
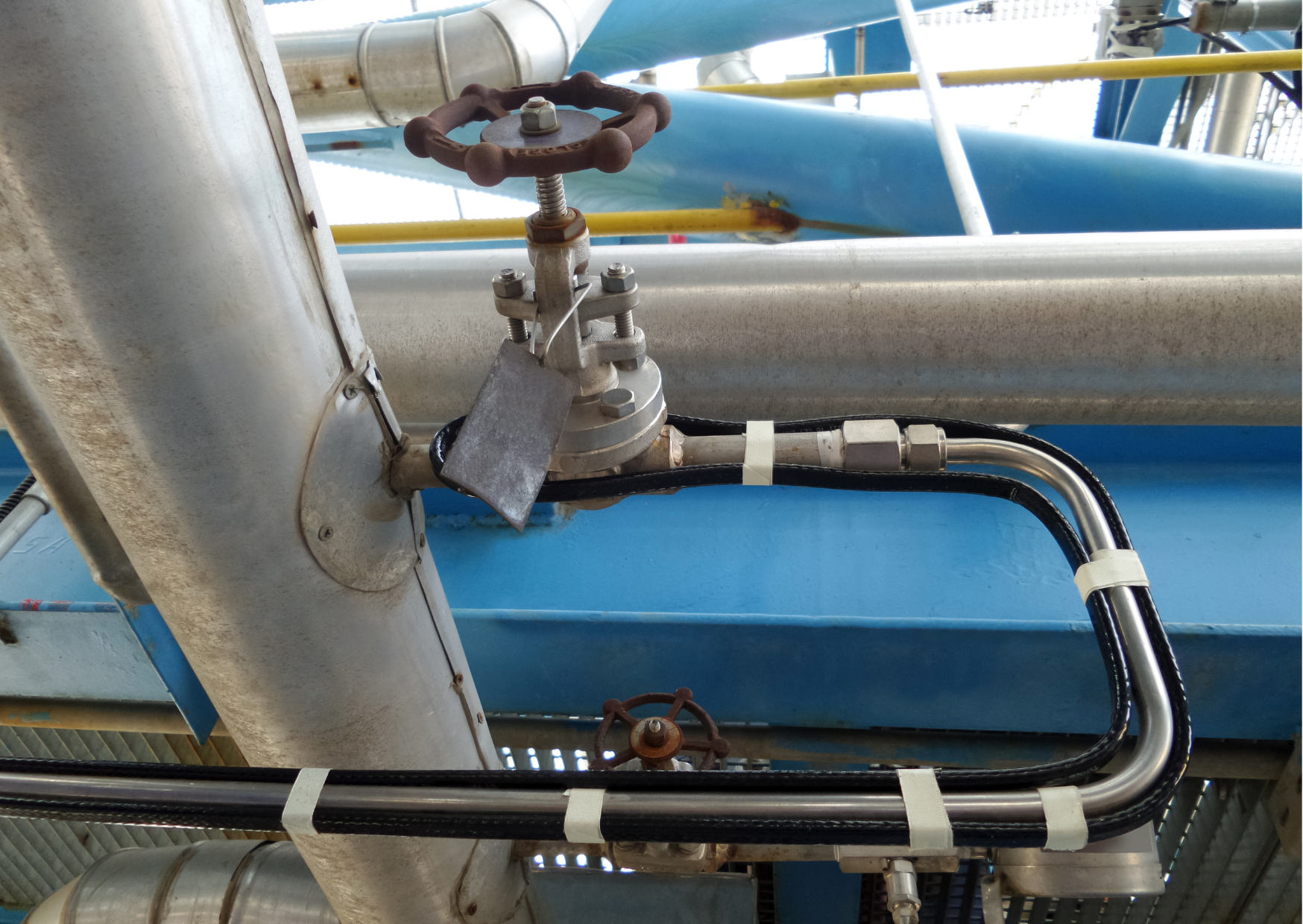
In a self-regulating heat trace system, the heat output is influenced by the surface temperature of where the heat trace is fitted. A warmer surface will lower the wattage output whilst a cooler surface will enable more wattage to be produced. Whilst this is a simple difference, understanding it is important when it comes to determining the right heat trace system for your application. A key benefit of self-regulating cable is that it can safely be overlapped on top of itself. This is unlike other forms of heat trace such as constant wattage or MI cable which develop a hot spot and burn out when overlapped or if it comes into contact with itself. Self-regulating cable won’t do that.
How self-regulating heat trace works
Self-regulating heat trace technology works by automatically altering power output in accordance with changes in the temperature that it is connected to. This technology starts on a microscopic level. The innermost part of the cable, typically called the conductive core, is made up of a carbon polymer that reacts to changes in temperature.
When the surface temperature goes down, the core contracts, increasing the total number of electrical paths, and as a result raising the temperature. On the other hand, as the outside temperature goes up, the core expands, lowering the number of electrical paths and reducing the cable’s final power output.
When do you need self-regulating trace heating products?
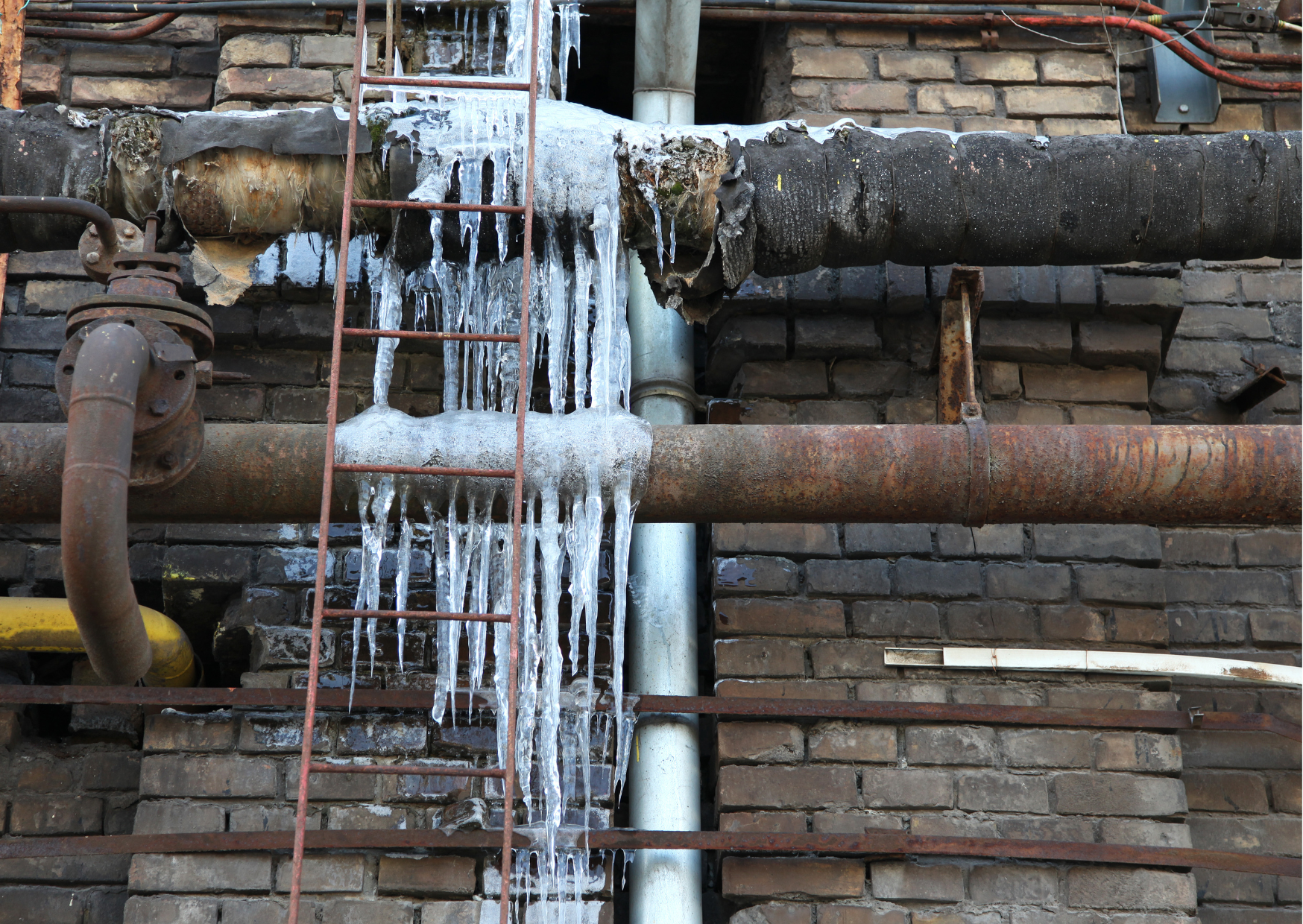
Even though it is a useful way to counter ice damage, thermal insulation by itself is not enough to offer full protection against pipes freezing up. In addition, pipes aren’t the only things that need protection in winter, cold weather can affect drains, sewers, roofs, gutters, and more.
There are alternatives, but a lot of them don’t have the same level of energy efficiency, safety, ease of installation, and maintenance-free operation that self-regulating heat trace cables have. A self-regulating trace heating system is highly effective in protecting buildings from the dangers of cold weather, whilst offering a range of other advantages too.
How long do heat cables last?
The life expectancy of trace heating cables mostly depends on how much they’re used, but 3-5 years is a common lifespan. Heat trace might carry on putting out heat, but the output can reduce over time, leaving you vulnerable to potential failure. Below are a few ways the lifespan of heat trace systems can be increased:
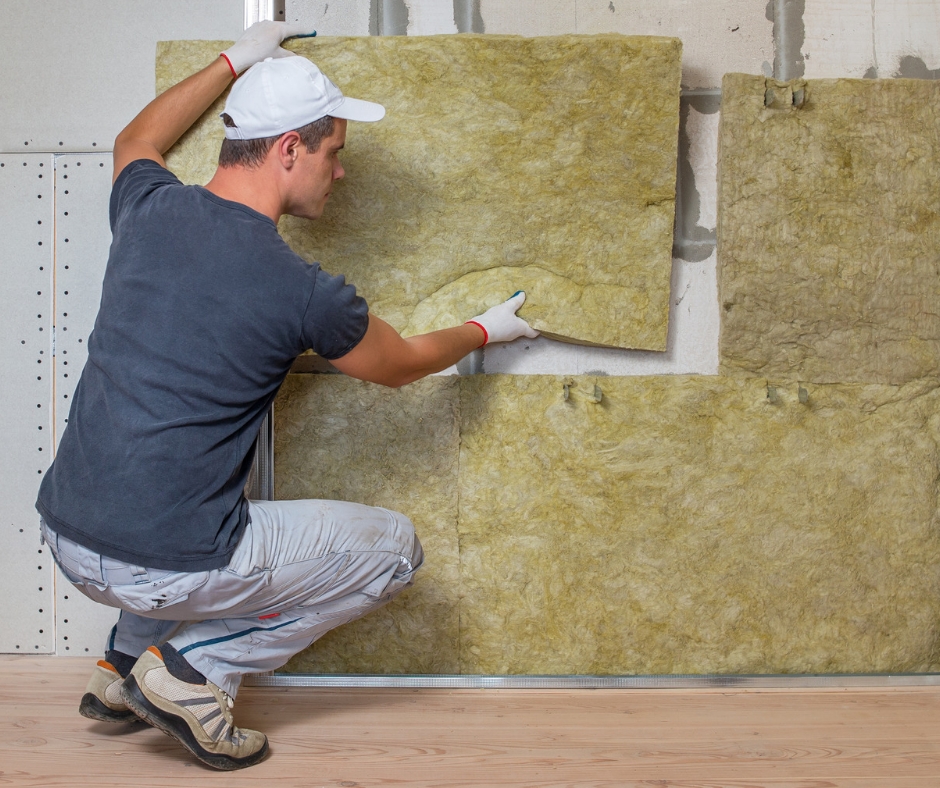
- Ensure your insulated jacket is well-fitted and high quality. A loose insulated jacket will increase the required power output and workload of the heat cable. No holes or gaps.
- Check that heat trace is properly installed over valves, flange pairs, supports, and any other items along the pipe. A heat trace specialist can help with this.
- Invest in thermostats and controllers. It still needs monitoring even though it is called self-regulating heat trace, as it can’t turn itself on or off.
How can TRM help?
As experienced and professional heat trace specialists, we can design, manufacture, install/train, and control complete heat tracing systems and heating solutions. This will compensate for heat losses on pipes, vessels, equipment, and more, which is essential to ensuring your operations stay efficient and safe no matter the weather and temperature. Contact us today to discuss your heat trace needs and find out how we can help with our full turnkey solutions.